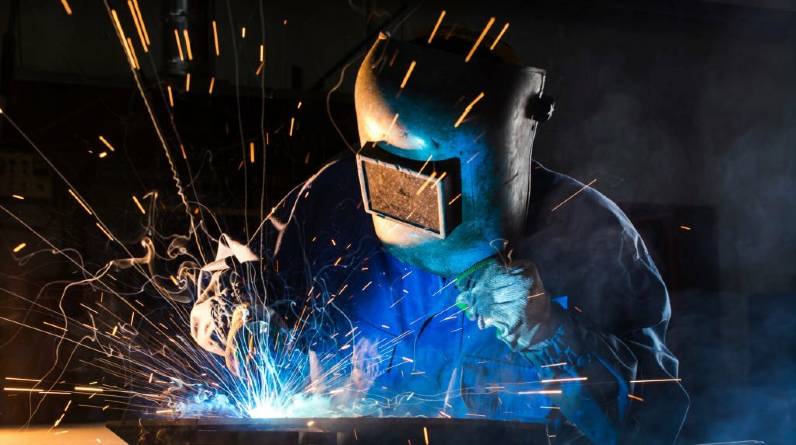
Welding is fundamental in various industries, from construction to manufacturing and artistry. The quality of a weld depends not only on the welder’s skills but also on the choice of the appropriate inert gas. This essential element protects the welding pool from atmospheric contamination, ensuring solid and clean welds. The significance of choosing suitable shielding gases for your welding project and the variables affecting this crucial choice will be discussed in this article.
Understanding Protective Shielding
These are gases used in welding to protect the molten metal from oxygen and other atmospheric elements that can lead to defects in the weld. They provide a protective barrier that ensures a stable arc, controls the bead shape, and influences the mechanical properties of the weld. The choice of inert gas largely depends on the welding process, the welded materials, and specific project requirements.
Types of Protective Shielding
There are two main categories of these gases: inert gases and active gases. Let’s delve into each type:
- Inert Gases: Inert gases like argon and helium are chemically stable and do not readily react with other elements. They are often used for welding non-ferrous metals like aluminium and magnesium. Argon, in particular, is famous for its ability to provide a stable arc and excellent coverage.
- Active Gases: Active gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and oxygen, are chemically reactive and can enhance the welding process. They are commonly used for welding carbon steel. CO2, for instance, can increase the penetration of the weld, making it suitable for thicker materials.
Factors Influencing Inert Gas Selection
Choosing the suitable inert gas for your welding project involves considering several crucial factors:
- Welding Process: Different welding processes, such as MIG (Metal Inert Gas), TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas), and FCAW (Flux-Cored Arc Welding), require specific shielding gases to achieve optimal results.
- Base Material: The type of metal you are welding plays a significant role. For instance, aluminium welding often requires pure argon as the inert gas, while carbon steel welding may use a mixture of CO2 and argon.
- Welding Position: The position you are welding (e.g., flat, horizontal, vertical, or overhead) can impact gas selection. Some gases provide better weld puddle control in specific positions.
- Welding Parameters: Adjustments to welding parameters, such as voltage, amperage, and wire feed speed, may be necessary when changing shielding gases to maintain weld quality.
- Cost Considerations: Some are more expensive, so cost-effectiveness is essential, especially for large-scale welding projects.
- Environmental Conditions: Factors like wind and drafts in the welding environment can affect gas coverage. In such cases, a heavier inert gas may be preferred.
- Welding Application: Different welding applications, such as structural welding, pipe welding, or precision welding, may have specific gas requirements to achieve the desired results.
- Joint Design: The design of the weld joint, including its geometry and accessibility, can influence inert gas selection. Some gases may be better suited for specific joint configurations.
- Welding Speed: The desired welding speed can impact gas choice. Faster welding speeds may require gases that provide deeper penetration and quicker solidification.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice of the appropriate welding gas is a critical determinant of weld quality, and it plays a pivotal role in various industries. Shielding gases, whether inert or active, create a protective barrier that safeguards the welding pool from atmospheric contaminants. Selecting the suitable gas hinges on several factors, including the welding process, base material, welding position, parameters, cost considerations, environmental conditions, application type, joint design, and welding speed. By carefully evaluating these variables, welders and project managers can ensure the successful execution of welding projects, delivering clean, solid welds that meet the desired specifications and standards across a wide range of applications.